Categorias do Blog
Dúvidas sobre algum produto?

IR Remote – Aprenda a fazer um controle remoto com arduino
IR Remote – Aprenda a fazer um controle remoto com arduino
Resumo
Como fazer isso, por favor consulte light led and how to connect cubieboard and arduino
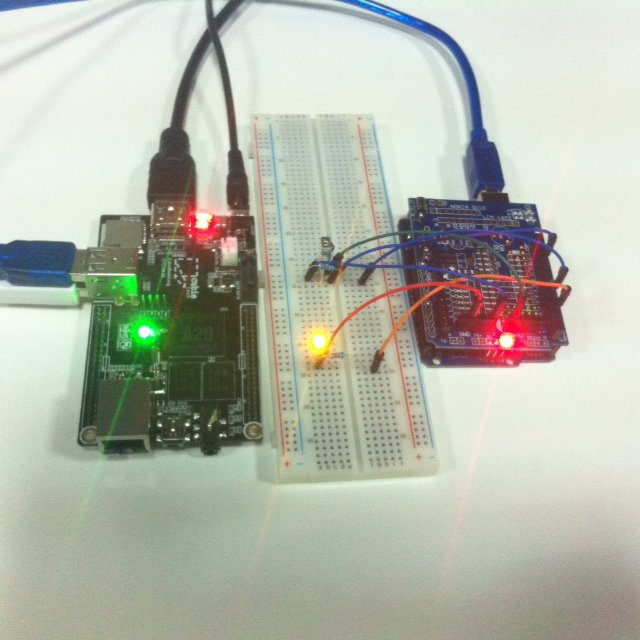
Headline
Source Code
/*
* Test send/receive functions of IRremote, using a pair of Arduinos.
*
* Arduino #1 should have an IR LED connected to the send pin (3).
* Arduino #2 should have an IR detector/demodulator connected to the
* receive pin (11) and a visible LED connected to pin 3.
*
* The cycle:
* Arduino #1 will wait 2 seconds, then run through the tests.
* It repeats this forever.
* Arduino #2 will wait for at least one second of no signal-----
* (to synchronize with #1). It will then wait for the same test
* signals. It will log all the status to the serial port. It will
* also indicate status through the LED, which will flash each time a test
* is completed. If there is an error, it will light up for 5 seconds.
*
* The test passes if the LED flashes 19 times, pauses, and then repeats.
* The test fails if the LED lights for 5 seconds.
*
* The test software automatically decides which board is the sender and which is
* the receiver by looking for an input on the send pin, which will indicate
* the sender. You should hook the serial port to the receiver for debugging.
*
* Copyright 2010 Ken Shirriff
* http://arcfn.com
*/
#include <IRremote.h>
int RECV_PIN = 11;
int LED_PIN = 3;
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN);
IRsend irsend;
decode_results results;
#define RECEIVER 1
#define SENDER 2
#define ERROR 3
int mode;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
// Check RECV_PIN to decide if we're RECEIVER or SENDER
if (digitalRead(RECV_PIN) == HIGH) {
mode = RECEIVER;
irrecv.enableIRIn();
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
Serial.println("Receiver mode");
}
else {
mode = SENDER;
Serial.println("Sender mode");
}
}
// Wait for the gap between tests, to synchronize with
// the sender.
// Specifically, wait for a signal followed by a gap of at last gap ms.
void waitForGap(int gap) {
Serial.println("Waiting for gap");
while (1) {
while (digitalRead(RECV_PIN) == LOW) {
}
unsigned long time = millis();
while (digitalRead(RECV_PIN) == HIGH) {
if (millis() - time > gap) {
return;
}
}
}
}
// Dumps out the decode_results structure.
// Call this after IRrecv::decode()
void dump(decode_results *results) {
int count = results->rawlen;
if (results->decode_type == UNKNOWN) {
Serial.println("Could not decode message");
}
else {
if (results->decode_type == NEC) {
Serial.print("Decoded NEC: ");
}
else if (results->decode_type == SONY) {
Serial.print("Decoded SONY: ");
}
else if (results->decode_type == RC5) {
Serial.print("Decoded RC5: ");
}
else if (results->decode_type == RC6) {
Serial.print("Decoded RC6: ");
}
Serial.print(results->value, HEX);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(results->bits, DEC);
Serial.println(" bits)");
}
Serial.print("Raw (");
Serial.print(count, DEC);
Serial.print("): ");
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if ((i % 2) == 1) {
Serial.print(results->rawbuf[i]*USECPERTICK, DEC);
}
else {
Serial.print(-(int)results->rawbuf[i]*USECPERTICK, DEC);
}
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println("");
}
// Test send or receive.
// If mode is SENDER, send a code of the specified type, value, and bits
// If mode is RECEIVER, receive a code and verify that it is of the
// specified type, value, and bits. For success, the LED is flashed;
// for failure, the mode is set to ERROR.
// The motivation behind this method is that the sender and the receiver
// can do the same test calls, and the mode variable indicates whether
// to send or receive.
void test(char *label, int type, unsigned long value, int bits) {
if (mode == SENDER) {
Serial.println(label);
if (type == NEC) {
irsend.sendNEC(value, bits);
}
else if (type == SONY) {
irsend.sendSony(value, bits);
}
else if (type == RC5) {
irsend.sendRC5(value, bits);
}
else if (type == RC6) {
irsend.sendRC6(value, bits);
}
else {
Serial.print(label);
Serial.println("Bad type!");
}
delay(200);
}
else if (mode == RECEIVER) {
irrecv.resume(); // Receive the next value
unsigned long max_time = millis() + 30000;
Serial.print(label);
// Wait for decode or timeout
while (!irrecv.decode(&results)) {
if (millis() > max_time) {
Serial.println("Timeout receiving data");
mode = ERROR;
return;
}
}
if (type == results.decode_type && value == results.value && bits == results.bits) {
Serial.println (": OK");
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
delay(20);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
}
else {
Serial.println(": BAD");
dump(&results);
mode = ERROR;
}
}
}
// Test raw send or receive. This is similar to the test method,
// except it send/receives raw data.
void testRaw(char *label, unsigned int *rawbuf, int rawlen) {
if (mode == SENDER) {
Serial.println(label);
irsend.sendRaw(rawbuf, rawlen, 38 /* kHz */);
delay(200);
}
else if (mode == RECEIVER ) {
irrecv.resume(); // Receive the next value
unsigned long max_time = millis() + 30000;
Serial.print(label);
// Wait for decode or timeout
while (!irrecv.decode(&results)) {
if (millis() > max_time) {
Serial.println("Timeout receiving data");
mode = ERROR;
return;
}
}
// Received length has extra first element for gap
if (rawlen != results.rawlen - 1) {
Serial.print("Bad raw length ");
Serial.println(results.rawlen, DEC);
mode = ERROR;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < rawlen; i++) {
long got = results.rawbuf[i+1] * USECPERTICK;
// Adjust for extra duration of marks
if (i % 2 == 0) {
got -= MARK_EXCESS;
}
else {
got += MARK_EXCESS;
}
// See if close enough, within 25%
if (rawbuf[i] * 1.25 < got || got * 1.25 < rawbuf[i]) {
Serial.println(": BAD");
dump(&results);
mode = ERROR;
return;
}
}
Serial.println (": OK");
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
delay(20);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
}
}
// This is the raw data corresponding to NEC 0x12345678
unsigned int sendbuf[] = { /* NEC format */
9000, 4500,
560, 560, 560, 560, 560, 560, 560, 1690, /* 1 */
560, 560, 560, 560, 560, 1690, 560, 560, /* 2 */
560, 560, 560, 560, 560, 1690, 560, 1690, /* 3 */
560, 560, 560, 1690, 560, 560, 560, 560, /* 4 */
560, 560, 560, 1690, 560, 560, 560, 1690, /* 5 */
560, 560, 560, 1690, 560, 1690, 560, 560, /* 6 */
560, 560, 560, 1690, 560, 1690, 560, 1690, /* 7 */
560, 1690, 560, 560, 560, 560, 560, 560, /* 8 */
560};
void loop() {
if (mode == SENDER) {
delay(2000); // Delay for more than gap to give receiver a better chance to sync.
}
else if (mode == RECEIVER) {
waitForGap(1000);
}
else if (mode == ERROR) {
// Light up for 5 seconds for error
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
delay(5000);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
mode = RECEIVER; // Try again
return;
}
// The test suite.
test("SONY1", SONY, 0x123, 12);
test("SONY2", SONY, 0x000, 12);
test("SONY3", SONY, 0xfff, 12);
test("SONY4", SONY, 0x12345, 20);
test("SONY5", SONY, 0x00000, 20);
test("SONY6", SONY, 0xfffff, 20);
test("NEC1", NEC, 0x12345678, 32);
test("NEC2", NEC, 0x00000000, 32);
test("NEC3", NEC, 0xffffffff, 32);
test("NEC4", NEC, REPEAT, 32);
test("RC51", RC5, 0x12345678, 32);
test("RC52", RC5, 0x0, 32);
test("RC53", RC5, 0xffffffff, 32);
test("RC61", RC6, 0x12345678, 32);
test("RC62", RC6, 0x0, 32);
test("RC63", RC6, 0xffffffff, 32);
// Tests of raw sending and receiving.
// First test sending raw and receiving raw.
// Then test sending raw and receiving decoded NEC
// Then test sending NEC and receiving raw
testRaw("RAW1", sendbuf, 67);
if (mode == SENDER) {
testRaw("RAW2", sendbuf, 67);
test("RAW3", NEC, 0x12345678, 32);
}
else {
test("RAW2", NEC, 0x12345678, 32);
testRaw("RAW3", sendbuf, 67);
}
}Para baixar a versão em PDF, clique no link abaixo:
Posted in: Arduino





ENTRE EM CONTATO COM A LOJAMUNDI.

Assine nossa Newsletter! É gratuito!
Cadastre seu nome e email para receber novidades e materiais gratuitos da Lojamundi.
